What are AI Agents?

At OpenAI's 2025 DevDay, the company made one thing clear — the future of AI lies in agents. With the introduction of AgentKit and upgrades to Codex, OpenAI is moving beyond chat-based models to systems that can perceive, reason, act, and learn autonomously. The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence is moving beyond models that respond to prompts, giving rise to a new class of intelligent systems known as AI agents.
An AI agent is a software program that perceives its environment, processes information, and takes action to achieve specific goals. Unlike simple automation scripts that follow fixed rules, AI agents can make decisions dynamically based on context, data, and learning from previous outcomes.
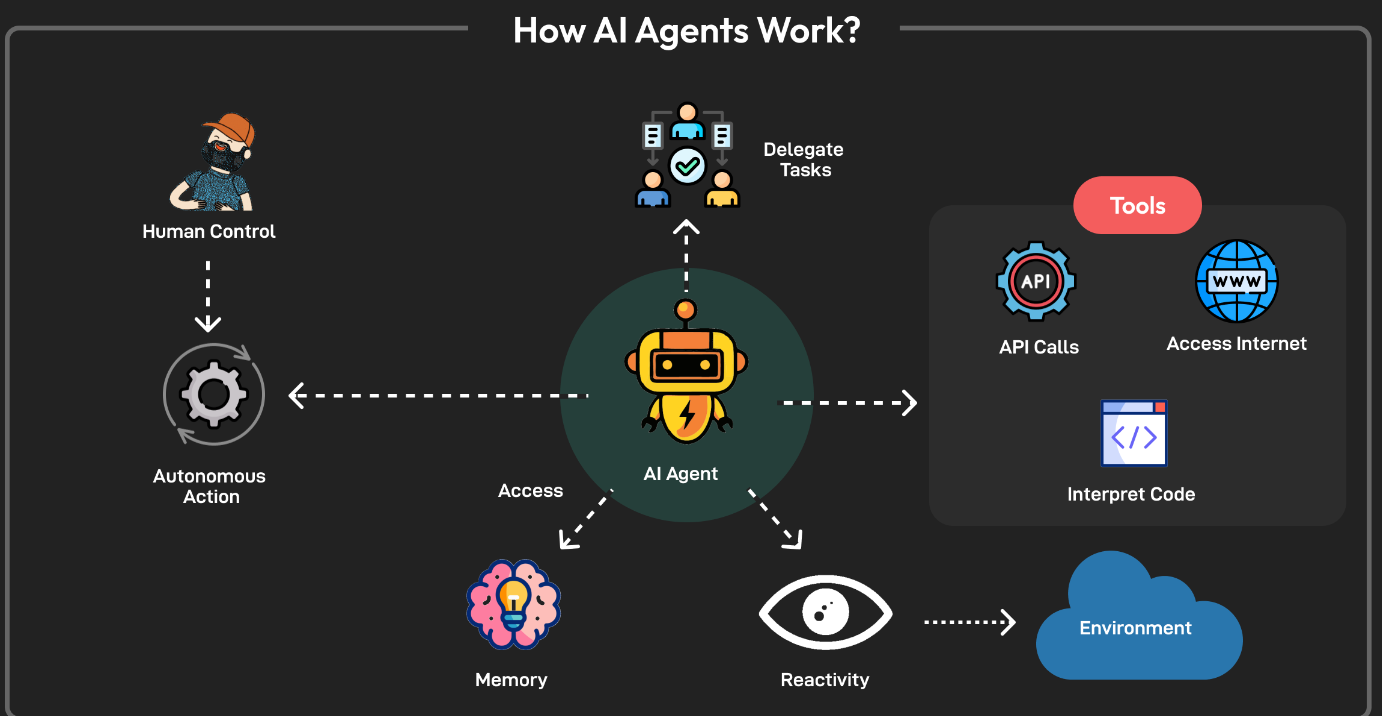
At their core, AI agents consist of four key components:
- Perception – The agent gathers data from its environment through sensors or APIs.
- Reasoning – It interprets that data, recognizes patterns, and decides what to do next.
- Action – The agent executes a task, such as replying to a user, sending an email, or adjusting a system setting.
- Learning – It evaluates the results of its actions and improves over time using machine learning.
These agents can exist in various forms — from rule-based systems to multi-agent systems that collaborate with other agents and humans.
The recent explosion of Large Language Models (LLMs), such as GPT-based systems, has further accelerated their capabilities, enabling agents to understand context, manage workflows, and even write or debug code.
Benefits of AI Agents
The rise of AI agents brings a range of benefits that extend across industries and personal productivity:
- Efficiency and Speed: AI agents can perform complex or repetitive tasks faster than humans. For instance, they can automate scheduling, data entry, or customer support 24/7.
- Scalability: Once built, an AI agent can handle thousands of simultaneous operations — making them ideal for businesses that need to scale without increasing headcount.
- Continuous Learning: Through machine learning, agents become smarter over time. They learn from user behavior, adapt to new data, and refine their decision-making processes.
- Cost Reduction: Automating routine tasks reduces labor costs and operational inefficiencies, allowing organizations to redirect human creativity toward high-impact work.
- Personalization: AI agents can deliver personalized experiences by analyzing user preferences, behaviors, and patterns — from tailored marketing to custom product recommendations.
Examples of AI Agents
AI agents are already transforming multiple domains. Here are a few practical examples:
- Healthcare: AI agents assist in diagnostics, patient monitoring, and personalized treatment recommendations.
- Finance: Fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and customer support use AI agents to improve security and efficiency.
- Manufacturing: Robots powered by AI agents manage assembly lines, quality control, and inventory.
- Education: Intelligent tutoring systems provide personalized learning paths and real-time feedback.
- Smart Homes: AI agents control lighting, security systems, and energy management based on user habits.
Use Case of AI Agents
A traditional, non-agentic chatbot can only provide static, pre-written answers to frequently asked questions. In contrast, an AI agent in the same role can handle a complex, multi-step issue. For instance, if a customer reports an undelivered order, the agent can:
- Access the company's database to retrieve the customer's order history and shipping details.
- Use a web search tool to check the real-time status of the shipping carrier.
- Identify that the package is delayed and proactively draft a personalized response that explains the situation.
- If the delay is significant, the agent can even initiate a refund process by calling the relevant internal API, all without human intervention. This level of service resolves issues 44% faster and increases the quality and consistency of support by 35%
Conclusion
AI agents represent a fundamental shift from tools that assist systems that act. By autonomously planning, reasoning, and executing complex tasks, they offer a powerful means to enhance productivity, improve accuracy, and drive innovation across every sector. As AI evolves, AI agents are becoming essential tools in multiple domains—from customer service to autonomous driving—promising enhanced efficiency and new possibilities.
References
- Meta AI - https://www.meta.ai/ (Writing Support)
- ChatGPT - https://chatgpt.com/ (Brainstorming)
- Claude AI - https://claude.ai/ (Writing Support)
- NapkinAI - https://www.napkin.ai/ (Image Creation)
Written by
Kenechukwu Chinegwu
Marketing Manager,
Zeta-AI
